(Rivista Internazionale - December 1994: Mind and brain are closer now - 2/3)
 |
Similar case as second graphic in previous page. The coloured chart, based on information contained in 16 recording points, shows the strong positivity (in dark blue) appearing on the brain, median and symmetrical, at the end of the discrimination. |
If the subject is engaged in a mental task, such as counting only the small frames, a clear positive potential appears after 300 msec (first graphic). Also here the famous time of 300 msec appears as it did for the reaction times.
This potential is interpreted as the reset of a cognitive process, that is, it marks the end of the operation.
A brain zone can easily carry out three of these discriminations a second. The more difficult the task, the later the potential will appear.
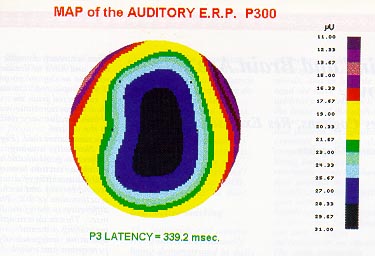
The P300 is independent of the sensory channel. The same happens when we have to discriminate between auditory stimuli, divided into frequent and rare events. The distribution is bilateral and symmetric, as can be clearly seen in the coloured chart (second graphic).
In pathological conditions,
for example after the destruction of tissue because of an apoplectic attack in a brain hemisphere, the P300 might not appear or have a pathologic conformation (see graphic next page).
N400
If P300 means a positive potential at 300 msec, the N400 potential of neurophysiology means a negative potential at 400 msec, that is later than P300, precisely because of what has just been said about the more complex tasks. This potential is not triggered by a discrimination, but by the semantic congruity of a phrase, and is therefore the electrical translation of an aspect of language. It is recorded when the last word of a phrase is not consistent with the previous message. For example, in the phrase «the boat passed under the bridge» there is a clear congruity and the potential does not form; but in the phrase «the
children are in the garden throwing voices» the last word is incompatible with the others and the potential in question appears 400 msec after the delivery of the word. Naturally, the delivery of the voice is followed electronically for obvious problems of synchronization
with the «averager» device which has to calcolate the
average of the responses. The N400 potential is not a lusus naturae, but a chance to check if patients who do not respond to external stimuli, as in some causes of head injuries or subarachnoid haemorrhage, are able to understand. The patient is lying there with his eyes open: can he understand? The recording of a N400 would tell us that he does.
 |
In this chart the colours on the right side correspond to the right hemisphere and vice versa. Note the relative conservation of the P300 to the right and its disappearance to the left on the damaged hemisphere. |
Retroactive masking
The importance of pattern recognition is continually being demonstrated in daily life.
Adults, children and animals recognize common objects in their environment. A well-known place is identified, just as infants recognize their parents'face and dogs their food bowls. Objects are only one type of the many models which people identify in environmental stimulation. For example, to understand language we have to recognize
phonemes, which correspond to significant words, and to be able to read we have to recognize arbitrary models such as the letters
of the alphabet. These examples indicate that pattern recognition is essential for almost all conscious activities. Every living being has to recognize models when they interact in a significant manner with his own world.
Interference in perception occurs when two stimuli are sent in rapid succession to an observer.
The term «proactive masking» indicates disturbance in the perception of the second stimulus because of the first, while the term «retroactive masking» indicates the interference of the second stimulus on the first (see graphic in the next page). Retroactive masking is a technique which consists of presenting a model, for example a figure, to the person, followed by
another insignificant stimulus which has the aim of disturbing the processing underway. Obviously, if the masking is very delayed the recognition occurs without difficulty, but if it is superimposed, the figure is not recognized; by gradually increasing the interval between the model and the masking one finds the minimum interval for avoiding the disturbing action of the masking. The role of the mask is to interrupt the processing of the real stimulus. The pattern can only be
identified by the subject if the processing is already complete before the arrival of the mask. The basic concept of the use of the mask is that the processing of the information content of a stimulus starts during the short physical exposition of the target (for example, 18 msec) and even lasts after it. This subsequent processing uses a persistence of the trace, which can even reach 100 msec in the case of a visual stimulus, the so-called «buffer» or «iconic memory».
Let us give an example: a subject needs 72 msec to identify a target. If it is shown for 18 msec, then the start of the masking must be delayed by at least 54 msec to
enable those 72 necessary for the identification. If the duration of the exposition of the stimulus were to be prolonged, the interval before the masking could theoretically be reduced by the same duration.
next page
back to previous page
back to summary